 |
Sydney (AFP) March 27, 2007 A cane toad the size of a small dog has been captured in the Australian tropical city of Darwin, the largest ever recorded in the country's remote Northern Territory, environmentalists said Tuesday. Green group FrogWatch said the monster male was 20.5 centimetres (8.1 inches long and weighed 861 grams (1.9 pounds). "The biggest toads are usually females but this one was a rampant male," said FrogWatch's Graeme Sawyer, who organises regular excusions to trap and destroy the feral pests blamed for destroying native Australian wildlife. "He is huge. I would hate to meet his big sister." The cane toad, whose scientific name is Bufo marinus, was introduced from South America in the 1930s to control another pest -- beetles that were ravaging the sugar cane fields of the tropical northern coasts. But the toads now number in the millions and are spreading westward through the Northern Territory, upsetting the country's ecosystem in their wake. Cane toads have poisonous sacs on the back of their heads full of a venom so powerful it can kill crocodiles, snakes or other predators in minutes. The animals, explosive breeders, have spread into the wetlands of world heritage Kakadu National Park and have recently become entrenched in Darwin. All attempts to fight the spread of the toads so far have failed and a history book last year rated their introduction as one of the greatest mistakes ever made in Australia.
Source: Agence France-Presse Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Related Links FrogWatch Darwin Today At TerraDaily.com Darwin Today At TerraDaily.com
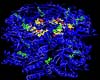 Nashville TN (SPX) Mar 27, 2007
Nashville TN (SPX) Mar 27, 2007An interdisciplinary team of researchers at Vanderbilt University has analyzed the simplest known biological clock and figured out what makes it tick. The results of their analysis are published in the March 27 issue of the journal Public Library of Science Biology. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |