 |
Heidelberg, Germany (SPX) Oct 29, 2004 When Darwin's skeptics attack his theory of evolution, they often focus on the eye. Darwin himself confessed that it was "absurd" to propose that the human eye evolved through spontaneous mutation and natural selection. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have now tackled Darwin's major challenge in an evolutionary study published this week in the journal Science. They have elucidated the evolutionary origin of the human eye. Researchers in the laboratories of Detlev Arendt and Jochen Wittbrodt have discovered that the light-sensitive cells of our eyes, the rods and cones, are of unexpected evolutionary origin � they come from an ancient population of light-sensitive cells that were initially located in the brain. "It is not surprising that cells of human eyes come from the brain. We still have light-sensitive cells in our brains today which detect light and influence our daily rhythms of activity," explains Wittbrodt. "Quite possibly, the human eye has originated from light-sensitive cells in the brain. Only later in evolution would such brain cells have relocated into an eye and gained the potential to confer vision." The scientists discovered that two types of light-sensitive cells existed in our early animal ancestors: rhabdomeric and ciliary. In most animals, rhabdomeric cells became part of the eyes, and ciliary cells remained embedded in the brain. But the evolution of the human eye is peculiar � it is the ciliary cells that were recruited for vision which eventually gave rise to the rods and cones of the retina. So how did EMBL researchers finally trace the evolution of the eye? By studying a "living fossil," Platynereis dumerilii, a marine worm that still resembles early ancestors that lived up to 600 million years ago. Arendt had seen pictures of this worm's brain taken by researcher Adriaan Dorresteijn (University of Mainz, Germany). "When I saw these pictures, I noticed that the shape of the cells in the worm's brain resembled the rods and cones in the human eye. I was immediately intrigued by the idea that both of these light-sensitive cells may have the same evolutionary origin." To test this hypothesis, Arendt and Wittbrodt used a new tool for today's evolutionary biologists � "molecular fingerprints". Such a fingerprint is a unique combination of molecules that is found in a specific cell. He explains that if cells between species have matching molecular fingerprints, then the cells are very likely to share a common ancestor cell. Scientist Kristin Tessmar-Raible provided the crucial evidence to support Arendt's hypothesis. With the help of EMBL researcher Heidi Snyman, she determined the molecular fingerprint of the cells in the worm's brain. She found an opsin, a light-sensitive molecule, in the worm that strikingly resembled the opsin in the vertebrate rods and cones. "When I saw this vertebrate-type molecule active in the cells of the Playtnereis brain � it was clear that these cells and the vertebrate rods and cones shared a molecular fingerprint. This was concrete evidence of common evolutionary origin. We had finally solved one of the big mysteries in human eye evolution." Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Related Links European Molecular Biology Laboratory SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express Dirt, rocks and all the stuff we stand on firmly
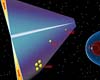 Paris (ESA) Jan 12, 2006
Paris (ESA) Jan 12, 2006Using the ESA Cluster spacecraft and the NASA Wind and ACE satellites, a team of American and European scientists have discovered the largest jets of particles created between the Earth and the Sun by magnetic reconnection. This result makes the cover of this week's issue of Nature. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |