 |
Manchester, UK (SPX) Feb 24, 2005 A British-led team of astronomers have discovered an object that appears to be an invisible galaxy made almost entirely of dark matter - the first ever detected. A dark galaxy is an area in the universe containing a large amount of mass that rotates like a galaxy, but contains no stars. Without any stars to give light, it could only be found using radio telescopes. It was first seen with the University of Manchester's Lovell Telescope in Cheshire, and the sighting was confirmed with the Arecibo telescope in Puerto Rico. The unknown material that is thought to hold these galaxies together is known as 'dark matter', but scientists still know very little about what that is. Dr. Jon Davies, one of the team of astronomers from Cardiff University, says; "The Universe has all sorts of secrets still to reveal to us, but this shows that we are beginning to understand how to look at it in the right way. It's a really exciting discovery!" When astronomers observe the visible Universe it is like looking out at the darkest night from a well-lit room. It is easy to see the street lights, car headlights and other well-lit rooms, but not the trees, the hedges and the mountains because they don't emit any light. We live on a planet close to a star, so as astronomers our observing 'room' is always well-lit. This can make it difficult to find the dark, hidden objects. The international team from the UK, France, Italy and Australia has been searching for dark galaxies using not visible light, but radio waves. They have been studying the distribution of hydrogen atoms throughout the Universe. Hydrogen gas releases radiation that can be detected at radio wavelengths. In the Virgo cluster of galaxies they found a mass of hydrogen atoms a hundred million times the mass of the Sun. The Virgo cluster is a large group of galaxies about 50 million light years away. Dr Robert Minchin from Cardiff University is one of the UK astronomers who discovered the mysterious galaxy, named VIRGOHI21. He explains, "From the speed it is spinning, we realised that VIRGOHI21 was a thousand times more massive than could be accounted for by the observed hydrogen atoms alone. If it were an ordinary galaxy, then it should be quite bright and would be visible with a good amateur telescope." Similar objects that have previously been discovered have since turned out to contain stars when studied with high-powered optical telescopes. Others have been found to be the remnants of two galaxies colliding. However, when the scientists studied the area in question using the Isaac Newton Telescope in La Palma, they found no visible trace of any stars, and no nearby galaxies that would suggest a collision. The astronomers first took observations of the dark object back in 2000 and it has taken almost five years to rule out all the other possible explanations. VIRGOHI21 appears to be the first dark galaxy ever detected. Professor Mike Disney, a member of the team said: "As Sherlock Holmes famously said, 'When you have eliminated the impossible, whatever is left - however improbable - must be the truth'" Astronomers have been measuring the way in which stars and galaxies move for many years. These measurements indicate that there must be far more matter in the Universe than can be accounted for by the visible light we see. This 'dark matter' still holds many mysteries for astronomers - is it well mixed up amongst the stars, or is it separate from the stars? Another puzzle is that the current ideas about how galaxies form predict that there should be many more galaxies in the Universe than are visible to us. So, these two ideas - dark matter and the lack of galaxies - have led some astronomers to predict that there must be unseen 'dark' galaxies hidden in the Universe. Finding a dark matter galaxy is an important breakthrough because, according to cosmological models, dark matter is five times more abundant than the ordinary (baryonic) matter that makes up everything we can see and touch. The presence of dark matter in the Universe can be inferred by looking at the rotation of galaxies and measuring how fast their visible components are moving. The amount of matter in a galaxy dictates the gravitational force needed to hold it together. Astronomers have seen galaxies where the material is moving so fast that they should fly apart - as they don't, there must be a stronger gravitational force acting than can be accounted for using visible matter. This has led astronomers to believe that there is more matter unseen - the mass of this 'dark matter' can be calculated from the gravitational force that must be acting to hold the galaxy together. Dark galaxies are thought to form when the density of matter in a galaxy is too low to create the conditions for star formation. The observations of VIRGOHI21 may have other explanations, but they are consistent with the hydrogen being in a flat disc of rotating material - which is what is seen in ordinary spiral galaxies. The Cardiff-led team hope to continue their unique observations to probe the hidden extent of the Universe that we live in. Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Related Links University of Manchester Jodrell Bank Observatory Cardiff University SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express Nuclear Space Technology at Space-Travel.com
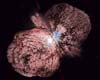 Boulder CO (SPX) May 31, 2005
Boulder CO (SPX) May 31, 2005Astronomers using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope have imaged a giant molecular cloud being shredded by howling stellar winds and searing radiation, exposing a group of towering dust pillars harboring infant stars, according to a University of Colorado at Boulder researcher. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |