 |
United Nations (AFP) Sept 23, 2007 World leaders were gathering here Sunday for an unprecedented UN summit aimed at whipping up action against climate change. About 150 countries are taking part in Monday's one-off event, some 80 of them at the level of heads of state and government, United Nations sources said. The meeting has been called by UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon, who has declared global warming one of the top priorities of his mandate. The summit aims at breaking a crippling deadlock in efforts to craft a global treaty on greenhouse gases, but diplomats discounted that it would be a session where leaders would spell out detailed emissions cuts. With rare exceptions, industrialized countries -- the economies most under pressure to promise cuts -- are represented by ministers, not by prime minister or president. "It will be interesting to see what they have to say, and how far they will go," said one source. Participants can speak at one of four parallel sessions, whose themes are emissions curbs; adapting to climate change; clean technology; and financing. Ban will close it with a summary of the main points, and follow this by hosting a dinner of "around 20" representatives from the world's biggest carbon-polluting economies, said a UN source. Scientists this year issued a grim warning, saying that climate change is already on the march and is bound to worsen this century, heightening the risk of hunger, drought, flood and violent storms. Green groups are lobbying for the UN meeting to breathe life into the flagging process to negotiate deeper cuts under the Kyoto Protocol -- a landmark treaty that, under its present commitments, will not even dent the greenhouse-gas problem. Talks on deeper commitments beyond 2012 take place in Bali, Indonesia, from December 3-14 under Kyoto's parent treaty, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). The task is to build a roadmap to a new global deal that will be concluded in 2009, giving signatories enough time to ratify it for the 2012 deadline. In theory, the treaty would accelerate cuts by industrialized countries, which account for 70 percent of the carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere today, and spur emissions mitigations by emerging giant economies, the major polluters of tomorrow. But achieving that will be an arduous task, complicated by the need to grapple for consensus and the fact that the United States, the world's No. 1 polluter, remains outside the Kyoto process. President George W. Bush opposes Kyoto on the grounds that it would be too costly for the US economy and unfair, as it is based on binding caps for developed countries but none -- so far -- for developing economies. But, under pressure at home and abroad, Bush this year signed up to the Group of Eight's (G8s) summit declaration that identified climate change as a "long term challenge" with the potential "to seriously damage our natural environment and the global economy." On Thursday and Friday, Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice will host a meeting in Washington of the world's 16 biggest polluters, plus representatives the European Union (EU) and the United Nations. Together these economies represent around 90 percent of global emissions. Initiated by Bush, the meeting will launch a 15-month process by which these economies can spell out what they intend to do on climate change and explore technological paths and industrial sectors that could achieve relatively quick and painless cuts in emissions. Green critics are suspicious, seeing in it as an attempt to seize the climate-change agenda and steer a US program of voluntary, unambitious cuts. Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Related Links All about the Ozone Layer
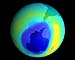 Montreal (AFP) Sept 21, 2007
Montreal (AFP) Sept 21, 2007Governments meeting in Montreal reached Friday an "historic" agreement to speed up the elimination of ozone-depleting chemicals, a UN spokesman said. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |