 |
Cape Canaveral FL (SPX) Nov 12, 2004 NASA's Deep Impact spacecraft arrived in Florida on Oct. 23 to begin final preparations for launch on Dec. 30. The spacecraft was shipped from Ball Aerospace & Technologies in Boulder, Colo., to the Astrotech Space Operations facility located near the Kennedy Space Center. Deep Impact was removed from its shipping container and is now undergoing its Functional and Mission Readiness testing, scheduled for completion on November 23 These tests involve the entire spacecraft flight system (including the flyby and impactor, associated science instruments and the spacecraft's basic subsystems), along with loading updated flight software. The high gain antenna used for spacecraft communications will be installed on Nov. 29. The solar array will then be stowed and an illumination test performed as a final check of its performance on Nov. 30. Deep Impact will then be ready to begin preparation for fueling on Dec. 6 and is scheduled to be completed on Dec. 9. The stacking of the Boeing Delta II launch vehicle on Pad 17-B will begin on Nov. 22 with the hoisting of the first stage into the launcher. Hoisting of the nine strap-on solid rocket boosters, in sets of three, is scheduled for Nov. 23, Nov. 29, and Dec. 1. The second stage will be hoisted into position atop the first stage on Dec. 3. The overall Deep Impact mission management for this Discovery class program is conducted by the University of Maryland in College Park, Md. Deep Impact project management is handled by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. The spacecraft has been built for NASA by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corporation. Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Related Links Deep Impact mission at JPL SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express Asteroid and Comet Impact Danger To Earth - News and Science
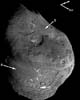 College Park MD (SPX) Sep 07, 2005
College Park MD (SPX) Sep 07, 2005Painting by the numbers is a good description of how scientists create pictures of everything from atoms in our bodies to asteroids and comets in our solar system. Researchers involved in NASA's Deep Impact mission have been doing this kind of work since the mission's July 4th collision with comet Tempel 1. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |